COMPUTER SCIENCE
Speech segmentation is the process of dividing speech signals into parts, which is an important aspect of speaker identification and speech recognition systems. This process improves the efficiency of the system by accurately detecting the beginning and end of speech. The use of voice activity detectors (VADs) plays an important role in segmentation, as they help to determine the boundaries between speech and silence. However, the most common errors in segmentation are false positives and false negatives, which negatively affect the overall accuracy of the system. In this regard, it is necessary to reduce errors through various approaches and methods. Measures such as reducing background noise, using deep learning models, and data augmentation can significantly improve the quality of segmentation. Using spectral analysis methods and features allows you to clearly distinguish between speech and background noise. The purpose of this study is to optimize the segmentation process and analyze the probability of errors, improve the efficiency of speech recognition systems. As a result, this work provides a basis for new research and development in the field of speech recognition. The article considers the problem of speech segmentation for speaker identification. The paper describes possible segmentation criteria – qualitative and quantitative characteristics of sound speech, such as speech delays and intonation, as well as their acoustic relationship. This allows a specialist to identify specific segment units (syllables, words, etc.), record their structure, and identify the main features.
This paper proposes the Decision-Making and Trial Evaluation Laboratory (DEMATEL) method to assess the requirements of risk factors in the supply chain of agricultural products. It can be said that the supply chain of agricultural products is the most vulnerable to various risks. The risks may differ depending on the area (operational, economic, social, and environmental). Our objective in this paper is to determine the importance of each risk factor and their interrelationships to prioritize the most significant risks for further eliminate or mitigate them. To achieve this, we used the DEMATEL method on a specific dataset and compared our proposed method with fuzzyDEMATEL. The results underscore that the central risk factor requirements revolve around Enhanced customer service and Controlling carbon emissions and pollution. Furthermore, we categorized the risk factors into two groups: cause and effect. Consequently, we noted slight variations between the outcomes of the methods, indicating the effective identification of critical risk factors by both approaches.
This study investigates the dynamics of social networks in the context of information confrontation between users. It introduces a simulation method for modeling these conflicts, which is based on game-theoretic and probabilistic approaches. The paper suggests a method for dynamically observing, following, and updating the status of the network. This innovative method conceptualizes information conflicts as a two-player game where the objective is to control as many network nodes as possible. By applying game theory, we formulated a strategy adaptation algorithm that allows each player to modify their decision-making based on the Facebook Researcher open dataset and current network conditions of its Kazakhstani segment. The method for tracking the network’s state dynamically leads to significant reductions in resource use and enhancements in computational efficiency. Comparative computational tests against other methodologies demonstrate the practical value of our approach for addressing a broad spectrum of challenges in information and analytical systems.
Currently, information technology is rapidly developing and one of its branches can be called machine translation. The use of machine translation in the process of understanding each other by people from different countries is increasing every year. At the moment, Google and Yandex machine translations are among the best machine translations. The quality of machine translation from Yandex and Google is improving every year. However, according to the results of the experiment, when translating from English or Russian into Kazakh and Turkic languages, the quality of the translation decreases. This was shown by the translation result obtained from these two machine translations in March 2024. After all, translation has also shown that it is directly related to the structure of language. Since 2000, scientists from the state of Kazakhstan have been actively studying translations into the Kazakh language. The goal of the work is to improve the quality of translation from English into Kazakh. For this purpose, a transforming model was created for the Kazakh and Turkic languages for learning translation in neural machine translation OpenNMT(). The created model studied and learned an English-Kazakh parallel corpus of 180,000 words. Later, the document with a structure of 20,000 different English sentences was translated into Kazakh. The result is measured using the Blue() metric. The translation result showed a high level. It is shown that in order to improve the results of the experiment carried out in the work during model training, it is necessary to increase the number of parallel corpora created from the English-Kazakh language pair.
Currently, information technology is rapidly developing and one of its branches can be called machine translation. The use of machine translation in the process of understanding each other by people from different countries is increasing every year. At the moment, Google and Yandex machine translations are among the best machine translations. The quality of machine translation from Yandex and Google is improving every year. However, according to the results of the experiment, when translating from English or Russian into Kazakh and Turkic languages, the quality of the translation decreases. This was shown by the translation result obtained from these two machine translations in March 2024. After all, translation has also shown that it is directly related to the structure of language. Since 2000, scientists from the state of Kazakhstan have been actively studying translations into the Kazakh language. The goal of the work is to improve the quality of translation from English into Kazakh. For this purpose, a transforming model was created for the Kazakh and Turkic languages for learning translation in neural machine translation OpenNMT(). The created model studied and learned an English-Kazakh parallel corpus of 180,000 words. Later, the document with a structure of 20,000 different English sentences was translated into Kazakh. The result is measured using the Blue() metric. The translation result showed a high level. It is shown that in order to improve the results of the experiment carried out in the work during model training, it is necessary to increase the number of parallel corpora created from the English-Kazakh language pair.
This paper presents the investigation of the process of optimizing the parameters of a PID controller using machine learning algorithms for the oil separation process control system. The optimization of the controller parameters (Kp, Ki, Kd) is important, in order to improve control quality and reduce the number of errors in dynamic processes. To solve this issue, several innovative methods were considered, such as the cuckoo search algorithm (CSA), the firefly algorithm (FA), particle swarm optimization (PSO), and the support vector machine (SVM). All the data, including the current process values (PV), setpoints (SP) and output signals (OP) were obtained from Tengizchevroil. In addition, the metrics, such as root-mean-square error (MSE), adjustment time, overshoot, and steady-state error were used to assess the effectiveness of optimized regulators. Overall, the results of the research indicate that there was a significant improvement of the dynamic characteristics of the system due to the usage of machine learning algorithms compared to the traditional approaches. The obtained parameters of optimization achieved the target value while being faster and more stable, thus increasing the productivity of control in the technological process.
With the rapid development of cities and their infrastructure, the demand for high-quality urban deliveries is increasing at the same rate. This work explores the possibilities of dynamically allocating delivery zones for courier deliveries based on data provided by the courier company. Traditional manually created delivery zones often do not ensure that the picture is relevant to the real situation in the city (weather, traffic, roads, etc.). This study presents the results of how K-Means and DBSCAN clustering algorithms can contribute to the dynamic distribution of delivery zones in clusters. The comparative analysis includes consideration of such indicators as Silhouette value and computational complexity of Big-O Notation. The results show that the K-Means algorithm creates structured and uniform clusters, while DBSCAN shows results in defining flexible clusters based on the density of data in the region. Multi-level DBSCAN provides an opportunity to reduce the concentration of “noise”, thereby increasing the coverage of all delivery points. The results obtained highlight the advantages of using clustering algorithms in creating dynamic delivery zones to improve the distribution of orders between couriers and reduce operating costs. Further research should include obtaining continuous real-time data flow to monitor the operation of algorithms in a dynamic environment.
Thermal imaging offers a non-invasive and robust approach to emotion recognition by capturing facial temperature patterns that correlate with psychophysiological states. This study investigates the application of deep neural networks to classify six basic human emotions – happiness, sadness, fear, disgust, anger, and surprise – using facial thermograms. A balanced dataset was collected under controlled experimental conditions, and four deep learning architectures were evaluated: Convolutional Neural Network (CNN), Fully Convolutional Network (FCN), EfficientNet, and MobileNet. The models were trained and tested on a curated set of preprocessed thermal facial images. Among the evaluated architectures, FCN achieved the highest classification accuracy of 90.04%. The results demonstrate that deep learning models, particularly FCNs, are well-suited for emotion recognition from thermal data, with potential applications in psychophysiological monitoring, healthcare, and real-time humancomputer interaction systems.
In this article, we explore the complexities surrounding token issuance within blockchain networks and their integration with decentralized exchanges (DEXs). With the swift evolution of cryptocurrency and blockchain technologies, token issuance has become a prevalent means of funding initiatives and creating novel digital assets. This journey involves tackling a spectrum of technical and organizational hurdles, ranging from choosing the right token standard to crafting, testing, and deploying smart contracts on the Ethereum blockchain. Further, we explore the integration of issued tokens with decentralized exchanges, highlighting the importance of such platforms in enabling token trading without reliance on centralized intermediaries. The technical solutions required for this integration, along with considerations of the unique aspects of exchange protocols, are critically analyzed. We pay special attention to the ERC-20 standard for token creation, detailing the process of smart contract development and deployment on the Ethereum network. Additionally, the advantages and limitations of integrating tokens with DEXs are examined, providing a comprehensive understanding of both the opportunities and challenges within the rapidly evolving digital asset ecosystem. This study extends the current understanding of token dynamics by incorporating an in-depth analysis of scalability challenges, cross-chain interoperability, and the evolving regulatory landscape affecting token issuance and trading. By offering practical recommendations for overcoming identified hurdles, this research guides practitioners and policymakers in navigating the complexities of the decentralized finance (DeFi) space, making a significant contribution to the field of blockchain technology and digital finance.
Adaptation of text generation style to specific audiences or content can be achieved without costly fine-tuning. We freeze model weights and instead (i) search eight decoder hyperparameters with Bayesian optimization and (ii) prepend a one-line style cue that modulates readability. Experiments on five mathematical question-answering benchmarks (AQUA-RAT, MathQA, GSM8K, MAWPS, SVAMP) with three 8–14 B-parameter checkpoints (LLaMA-3.1-8B, DeepSeek-Qwen-8B/14B) show that 50-trial Optuna searches raise exact-match accuracy by up to 36 percentage points and close 5–10 points of the gap to 30–70 B fine-tuned baselines. The same settings transfer across tasks with under 2-point loss. Adding the child-friendly header leaves accuracy virtually unchanged while halving the Flesch–Kincaid grade level and shortening reasoning traces. All experiments fit within a few GPU-hours on a single A100, making the method practical for resource-constrained deployments. The study demonstrates that careful decoder control combined with micro-prompts delivers numerical correctness and audience-appropriate exposition without additional training or tuning time.
MATHEMATICAL SCIENCES
It is known that the system of eigenfunctions of the classical biharmonic operator with the Dirichlet boundary condition is complete and orthonormal in space. The eigenvalues corresponding to these eigenfunctions are positive and can be numbered in ascending order. In some cases, eigenfunctions and eigenvalues of boundary value problems for a perturbed biharmonic operator have similar properties. In this work, a nonlocal analogue of the perturbed biharmonic operator is introduced using orthogonal matrices. Spectral problems of two boundary value problems are studied for this operator. Dirichlet boundary conditions are considered in the first problem, and Dirichlet-type conditions in the second. When studying the first problem, we use the complete system of eigenfunctions of the Dirichlet problem for the perturbed biharmonic operator. Using the properties of these systems, as well as the properties of the image with orthogonal matrices, we find the eigenfunctions and eigenvalues of the main problem. In the second task, we use the eigenfunctions and eigenvalues of the Dirichlet problem for the Laplace operator. Using the explicit form, as well as the properties of these systems, we construct the eigenfunctions and eigenvalues of the second task. The proof of the theorem on the completeness of the system of eigenfunctions of the considered tasks in space is provided.
Based on the results obtained by the authors in one of the previous articles (Bulletin of the Kazakh-British Technical University, 2024, 21(2), pp.127-138), the class of doubly close-to-convex in the unit disk 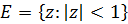
of the functions f(z), set using the conditions
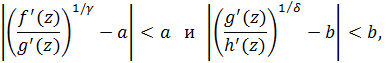
where the functions f(z), g(z) and h(z) have expansions of the form
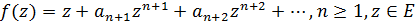
, and the function h(z) is convex. In this class, the theorems of distortion, rotation and radius of convexity are established. In particular cases, we obtain both a number of previously known and a number of new original results for doubly close-to-convex and close-to-convex functions. Based on this class, a class of doubly close-to-starlike functions is introduced, for which the growth theorem and the star radius are found. For specific values of the parameters previously known results for close-to-starlike functions are obtained.
A linear two-point boundary value problem for a system of integro-differential equations with a constant delay argument is investigated on a finite interval. By dividing the interval by parts, the integral term of the integrodifferential equation with constant delay argument is replaced by the quadrature formula. With this replacement, the linear two-point boundary value problem for a system of integro-differential equations with a constant delay argument is approximated by the linear boundary value problem for a system of loaded differential equations with a constant delay argument. Definitions of correct solvability of boundary value problem for system of integro-differential equations with delay argument and constructed boundary value problem for system of loaded differential equations with constant delay argument are introduced. Conditions of correct solvability of linear boundary value problem for system of integro-differential equations with delay argument and linear boundary value problem for system of loaded differential equations with delay argument are established. Relationship between correct solvabilities of linear two-point boundary value problem for system of integro-differential equations with constant delay argument and approximating linear two-point boundary value problem for system of loaded differential equations with constant delay argument is shown.
The aim of this work is to study a nonhomogeneous system of second-order partial differential equations that is close to the ordinary case. A particular solution of the considered system near the regular singular point (0,0) is sought in the form of a generalized power series in two variables using the Frobenius-Latysheva method. Various possible cases are demonstrated, where the systems of determining equations have simple or multiple roots. A theorem is presented for the particular solution of a “resonant” nonhomogeneous system of second-order partial differential equations. As an example, the solution of a nonhomogeneous Bessel system is given. The corresponding homogeneous system has solutions in the form of Bessel functions of two variables, while the particular solution of the nonhomogeneous system is expressed as a product of Bessel functions.
We study spectre of Turing degrees permitting to construct numbeings for the set of all linear orders isomorphic to the standard order of natural numbers. It is known that the index set of all linear orders isomorphic to the standard order of natural numbers is П3-comlete. This mean that this set has no computable numberings. In this work we show that the set of all linear orders isomorphic to the standard order of naturals has O’’-computable numbering, and has no O’-computable numberings. In the Bazhenov, Kalmurzayev and Torebekova’s work they construct universal c.e. linear preorder in the structure under computably reducibility. They use the following fact: there is computable numbering for some subset S0 of c.e. linear preorders such that any c.e. linear preorder lies in lower cone for some c.e. linear order from S0. We show that the similar fact is not hold for the structure of all linear orders isomorphic to the standard order of naturals. Moreover, for this structure there is no O’-computable numbering with simiral fact.
In this article, new anisotropic grand Lorentz spaces are defined and their propertөies are studied. These spaces are a new structure that provides a unified parameter for the study of various functional spaces. The consideration of grand spaces is especially important for the study of boundary conditions of parameters and allows us to achieve new results in this area. The study of boundary parameters in classical spaces is not always possible. In recent years, grand Lebesgue spaces and their generalizations have been widely studied in problems of functional spaces. These spaces are generalizations of classical Lorentz and grand Lorentz spaces. The article defines grand anisotropic Lorentz spaces, gives basic estimates in these spaces, proves embedding theorems, and derives embedding theorems for parameters. The results obtained can play an important role not only in theoretical, but also in applied problems.
The criteria for the fulfillment of continuous and discrete inequalities involving Hardy operators are one of the key problems in the theory of weighted inequalities. The study of discrete inequalities for the class of matrix operators can be considered a new direction of research. In general, since the stability criterion in the weighted Lebesgue space for a discrete operator with a matrix kernel is not defined, various conditions are imposed on the matrix, which allows for obtaining broader results compared to the case without a matrix. In this work, we consider discrete quasilinear operators with matrices satisfying certain conditions. The results obtained for quasilinear inequalities can be applied to the description of bilinear Hardy inequalities.
Fractional derivatives, due to their nonlocality, can describe complex processes where historical data are important for future calculations. At the same time, this property brings difficulties in numerical simulations. This paper presents a new discrete operator for approximating the fractional derivative based on the Grunwald-Letnikov definition, the "principle of short memory", memorization and analytical assumptions. This operator significantly reduces the number of operations in the process of calculations, when solving boundary value problems, due to the storage of calculated data and transformation for further use with adjustable accuracy.
The notion of o-minimality is highly productive for linearly ordered structures, but a direct transfer of this concept to partially ordered sets encounters certain difficulties. Indeed, there is a striking scarcity of works on o-minimal partially ordered structures. The standard definition of o-minimality for partially ordered structures states that every definable subset is a Boolean combination of intervals and points. However, since Boolean combinations involve the operation of taking set complements, and in partially ordered sets the complement of an interval can be extremely complex, this approach presents certain challenges for studying the resulting class of structures. We propose using an alternative definition of o-minimality: a partially ordered structure is o-minimal if every definable subset is a finite union of generalized intervals and points. In the paper, we provide a number of examples demonstrating that this definition is nontrivial and that there exist structures which are o-minimal in this new sense.
The aim of this study is to analyze the spatial and temporal distribution of temperature and air pollutant concentration in the urban atmosphere of Almaty using numerical modeling techniques. A two-dimensional advection-diffusion model was developed to simulate the diurnal dynamics across a territory of approximately 80 square kilometers. The model incorporates key physical processes such as wind-driven transport, turbulent diffusion, and localized emission sources that are typical of dense urban environments. Simulation results demonstrate a smoother spatial distribution of temperature, largely driven by solar radiation cycles, in contrast to highly localized peaks in pollutant concentrations associated with anthropogenic activities such as transportation and industry. These contrasting behaviors highlight the need for differentiated mitigation strategies. The findings of the study offer important insights for urban planning and the development of effective air quality management policies. The proposed model provides a practical tool for understanding environmental dynamics and evaluating the potential impact of pollution control measures in complex urban terrains.
This paper presents a numerical method for solving the convection-diffusion equation with a fractional-order Caputo derivative to model air pollution in urban environments. The developed finite element scheme accounts for memory effects, offering a more accurate representation of pollutant transport compared to classical models. Stability and convergence of the method are theoretically proven and supported by numerical experiments. The model effectively identifies pollutant accumulation zones and can forecast air quality under various weather conditions. The results have practical value for improving environmental monitoring systems and planning measures to reduce pollution levels.
PHYSICAL SCIENCES
Nobelium-activated strontium aluminate (Sr4-x-y CayAl14O25:Nox)was synthesized using boric acid by the solgel method in different concentrations. The samples obtained were heated in air at various temperatures, using the results of X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis, it was found that Sr4Al14O25 is single-phase at 1300°C. For partial replacement of strontium ions with calcium ions, the same strontium aluminate containing 0.04 mol/g of Nobelium was selected, and single-phase samples were obtained from a calcium concentration up to xCa=0,9. The highest relative intensity of the luminescence of Ho3+ ions in all samples was in the red zone of the spectrum, corresponding to the passage of these ions 5F5→5I8. In photoluminescence studies of samples, when excited by radiation with wavelengths of 465 nm and 560 nm, the maximum light emission of ~652 nm,~692 nm, and ~694 nm were formed. In all series of synthesized single-phase materials, the most intense light emission peaks are in the compound that exchanges Sr2+ strontium ions with Ca2+ ions. From the images taken using a scanning electron microscope (SEM), it can be seen that Sr4-xAl14O25:Hox particles are stuck together in monolithic blocks due to the use of extremely high heating temperatures. Although the synthesis of strontium replacement with calcium was carried out at the same temperature, changes in morphology were observed, and the hexagonal shape of aluminate particles partially replaced by Ca2+ ions was clearly visible.
The article looks at how to make sensitive parts for gas analyzers that work at room temperature using thin films of tin oxide (SnO2) that are deposited on glass substrates. Three precursor systems were employed: a solution of SnCl4*5H2O in ethanol, a hydrosol of tin hydroxide, and a combination of them. The films were formed by spray pyrolysis at 400°C. X-ray structural analysis and scanning electron microscopy were performed; it was found that the crystallite sizes were 6–13 nm. We studied the sensitivity of the films to water vapor. The highest sensitivity (R0/Rvapor = 3.75) and response time (less than 1 second) were observed in films obtained from the sol. When adsorption on t-SnO2 (001) and c-SnO2 (111) surfaces were modeled, it was found that the c-SnO2 structure is better for detecting carbon monoxide because it stays stable in high humidity. The results obtained are of interest in the development of new gas sensors.
This study examines the NGC 2516 open star cluster using numerical simulations and comparisons with observational data. By employing the phi-GRAPE-GPU code, we reconstructed the cluster’s orbit over 123 Myr to identify its birthplace within the Galaxy. Over 70 simulations were conducted, refining the initial parameters of the star cluster to better match present-day observations. The analysis revealed that the standard mass function parameters could not fully replicate the unique characteristics of NGC 2516. To address this, we adjusted the mass function to align more closely with the observed stellar properties. The results demonstrate morphological similarities between the simulated and observed clusters. However, the simulations also include additional tidal tail stars that are absent in observational data, possibly due to observational limitations. These findings highlight the need for more detailed analyses and comparisons. In future studies, we plan to apply machine learning techniques to more accurately identify and classify stars in the tidal tails.
This work presents the synthesis of hydrogenated amorphous diamond-like carbon (HDLC) films using a magnetron method in a gas mixture of CH4+Ar. The synthesis of the HDLC films was carried out over a wide temperature range from 80 °C to 240 °C. The local structure of the synthesized samples was studied using Raman spectroscopy. Additionally, the mechanical and optical properties of the obtained thin diamond-like carbon films were investigated. The dependence of the studied characteristics on the synthesis conditions was demonstrated. It was found that the substrate temperature significantly influences the formation of the structure and properties of hydrogenated diamond-like carbon films. The dependence of the bandgap on the substrate temperature was shown. It was revealed that the bandgap of the synthesized hydrogenated samples decreases from 1.78 eV to 1.63 eV as the temperature increases from 80°C to 240°C. This can be attributed to the increase in sp² hybridized bonds and the growth of π-electron density states. It was also shown that the change in microhardness of hydrogenated diamondlike carbon films correlates with the change in optical bandgap. Microhardness, evaluated using the Knoop method, was found to range from 37.5×10² kgf/mm² to 29.5×10² kgf/mm², depending on the substrate temperature. This change in microhardness confirms the decrease in sp³ hybridized bonds in the film structure.
This study presents a methodology for the fabrication and investigation of the electrical capacitance properties of zirconium dioxide (ZrO2)-based nanopowders doped with 3 mol.% yttrium oxide (Y2O3). The main focus is on the creation of dense compacts using high hydrostatic pressure up to 500 MPa, as well as the optimization of the technique for applying electrical contacts to ensure measurement stability. The experimental section describes a setup that enables the recording of discharge characteristics of the samples in a temperature range from 30 to 400 °C. The article provides data on the dependence of capacitance on circuit resistance and applied voltage, as well as the influence of thermal treatment – specifically annealing at 400 °C and 500 °C – on structural and capacitive parameters. It is demonstrated that under optimal conditions – namely, a voltage of 10 V, a resistance of 10 kΩ, and air humidity of 50% – a maximum capacitance of up to 1256.948 µF is achieved. The study also shows that increasing the annealing temperature improves the capacitive properties, which is attributed to changes in the material’s microstructure. The presented results highlight the potential of YSZ nanopowders in developing solid-state nanoionic energy storage devices with high energy density, making them promising candidates for use in energy storage systems and microelectronics.
Population growth, economic and industrial development contribute to the growth of human energy consumption. The photoelectrochemical hydrogen production is one of the most environmentally friendly and costeffective technologies that can maintain the balance between the energy produced and consumption. Therefore, the study of materials in this direction and their improvement, increasing efficiency and stability, is an important scientific and technical task. Photoactive semiconductors (PS) absorb solar energy and convert it directly into chemical energy separating hydrogen and oxygen from water molecules. The article discusses the principle and mechanism of the photoelectrolysis process, the main requirements for materials, and the latest innovations in this direction. The water-splitting reaction, main parameters, and concepts are explained. Analyzing the latest results, the efficiency of converting sunlight into hydrogen was compared and analyzed. The main conclusion is that the efficiency of the photoelectrochemical cells depends on the quality, complexity, and configuration of the materials.
OIL AND GAS ENGINEERING, GEOLOGY
The territory of Northern Ustyurt, which has a complex geological structure, has long attracted the attention of researchers. In recent years, a significant amount of seismic exploration work, both 2D and 3D, has been carried out on the territory of Northern Ustyurt. Structural constructions were made for target reflecting horizons and the geological structure of the studied areas for the Paleogene-Triassic sediment complexes was studied quite fully. The Shagyrly-Shomyshty gas field is located within the North Ustyurt Depression, the northwestern marginal zone of the Kosbulak trough, was discovered in 1959. In 2015 the field was put into industrial development. At the early stages of development of the Shagyrly-Shomyshty deposit, it was believed that it was confined to an anticline fold with four pronounced arches. However, based on the results of geological and geophysical work carried out to date, a completely different conceptual view of the geological structure of the deposits has been proposed and substantiated. This became possible due to the use, along with structural, of dynamic interpretation of seismic data, the purpose of which is to predict reservoir properties and fluid saturation of the host rocks. The article presents the results of dynamic interpretation of seismic data, which allowed for a more detailed study of the structure, the creation of a substantiated geological model and recommendations for further development of the field.
CO2 flooding, as a commonly employed enhanced oil recovery (EOR) method today, is characterized by high oil displacement efficiency, environmental friendliness, and economic viability, and has been extensively developed and applied in oil and gas field development. During CO2 flooding operations, gas channeling frequently occurs within the reservoir due to significant permeability contrasts arising from formation heterogeneity, coupled with the low density and viscosity of CO2. This phenomenon can adversely affect the normal productivity of oil wells. With the advancement of CO2 flooding technology, the effective prevention of CO2 channeling has become crucial for improving oil recovery. Gel particle plugging systems, being economically viable and efficient, exhibit favorable stability, adaptability, and strength, leading to significant applications in oilfield development and demonstrating promising prospects for future development. This paper comprehensively reviews the classification and developmental status of gel particle systems used for channeling control in CO₂ flooding. It introduces the mechanisms of several gel particle types, including preformed particle gel, polymer microspheres, and dispersed particle gel, and examines their current development status both domestically and internationally. Furthermore, future research directions and application prospects are discussed.
Today, there is a growing demand for environmentally safe, recyclable, and highly durable materials for modernizing railway infrastructure using industrial waste generated from the purification of sulfur gases in gas fields. The high CO2 emissions and hydrophilic properties of traditional cement-based concretes are limiting their use in long-term and aggressive environments. In light of this, the present study explored the prospects of using sulfur-based concretes with hydrophobic, chemically stable, and thermoplastic properties in railway sleepers. Samples obtained from compositions consisting of molten sulfur, modified stabilizers, basalt fiber, and nanoadditives were analyzed using TGA/DTA and IR spectroscopy methods. Important physicochemical properties such as compressive strength, water absorption coefficient, thermal conductivity, and resistance to mechanical wear were evaluated through laboratory and industrial tests. The research results demonstrated that sulfur concrete could be implemented not only as an alternative cement-free solution but also as a sustainable, long-lasting, and recyclable structural material for future railway sleepers.
Carbon capture, utilization, and storage (CCUS) technologies have become critical tools in mitigating anthropogenic greenhouse gas emissions and achieving global climate targets. This study investigates the potential for CO₂ sequestration in the depleted gas reservoirs of the Tengiz field, a unique site characterized by deep reservoir conditions and a history of extensive hydrocarbon extraction. The research aims to evaluate the technical feasibility and effectiveness of CO₂ injection into a high-temperature, high-pressure formation, using dynamic reservoir simulation. Key objectives include assessing injection capacity, breakthrough time, storage efficiency, and pressure behavior under varying operational scenarios. The study integrates geological, petrophysical, and fluid data to build a robust sector model, calibrated with historical production data. Simulation results demonstrate favorable injectivity and containment, with minimal risk of CO₂ leakage. These findings contribute to the growing body of knowledge on field-scale CCUS deployment and support the development of sustainable carbon management strategies in mature oil and gas provinces.
ECONOMY AND BUSINESS
To delve deeper into how green credit influences the performance of China’s listed commercial banks, this study investigates 16 publicly listed banks as research samples. The study aimed to analyze the impact of Green Credit on the Operational Performance of Chinese Listed Commercial Banks. The performance levels of these banks are assessed using factor analysis, and the effects of green credit are examined through fixed-effects and moderating effect models. The results suggest that, given the relatively recent adoption of green credit policies and the still-developing institutional framework in China, green credit currently shows a negative association with bank performance. Moreover, corporate social responsibility (CSR) plays a moderating role that amplifies this adverse effect. Nonetheless, in the long run, promoting green credit remains a necessary and inevitable direction. With ongoing improvements in green credit mechanisms, commercial bank performance is expected to improve, fostering both ecological sustainability and economic growth.
This study aims to explore the use of Artificial Intelligence in recruitment, focusing on its impact on decisionmaking, transparency, and trust. Artificial Intelligence has rapidly become a vital tool in modern recruitment processes, automating key tasks such as screening and interview scheduling. This research applies comprehensive analysis, utilizing both descriptive and network methodologies, to examine how Artificial Intelligence-driven recruitment affects stakeholders, particularly in terms of trust in Artificial Intelligence systems. The findings show key areas in the application of Artificial Intelligence in recruitment, including automated decision-making, stakeholder interaction, and the ethical concerns surrounding bias and transparency. Transparency not only enhances the perceived fairness of Artificial Intelligence processes but also builds trust among both recruiters and candidates. However, overreliance on Artificial Intelligence, especially without proper human oversight, may cause discomfort, leading to a potential erosion of trust. Artificial Intelligence helps organizations improve their recruitment outcomes, particularly in achieving diversity and minimizing biases. Artificial Intelligence in recruitment hinges on transparency, trust, and a balanced integration of Artificial Intelligence and human input. These insights are valuable for organizations looking to optimize their recruitment processes and foster trust in Artificial Intelligence-driven systems.
The present research study examines the problems and prospects of Kazakhstan’s tourism sector. By reviewing the current issues confronting the tourism industry and determining its potential for expansion and improvement, this research offers valuable perspectives that can guide actions intended to strengthen Kazakhstan’s standing as a sustainable and economically viable travel destination worldwide. A mixed-methods approach was administered to explore the problems and prospects in Kazakhstan’s international tourism, focusing on garnering the opinions of foreign tourists who have visited Kazakhstan. The researchers gathered the data from 206 foreign tourists by administering a well-structured and self-administered questionnaire. This study provided valuable information about Kazakhstan’s current state of the tourist business, highlighting both opportunities and challenges. The results indicated that travelers preferred specific locations over others, such as the Southern and Northern ones. The respondents stated that the three most pressing issues facing Kazakhstan’s tourist sector are infrastructure, marketing, and service quality. Despite these challenges, respondents highlighted Kazakhstan’s incredible natural beauty as a significant expansion opportunity for the travel industry. This study suggests a practical strategy for boosting passenger numbers and strengthening the country’s tourism industry. By providing a distinctive analysis of foreign and domestic tourism in Kazakhstan, this study advances the field of tourism studies. It stands out because it focuses only on the opportunities and difficulties of foreign travel in Kazakhstan. The study’s unique approach to comprehending the experiences and viewpoints of foreign visitors to Kazakhstan is rooted in its empirical methodology.
Business Process Modeling (BPM) plays a pivotal role in optimizing decision-making for targeted advertising in digital marketing. Traditional manual BPM models, reliant on human-driven workflows, face limitations in scalability, efficiency, and adaptability to dynamic market demands. This study aims to develop and evaluate a Human-AI Hybrid BPMN framework that integrates AI-driven automation with human expertise to enhance process adaptability, targeting precision, and regulatory compliance (e.g., GDPR, CCPA) for private advertising agencies in Kazakhstan [3, 9]. The methodology employs a comparative mixed-methods approach using BPMN diagramming tools (Bizagi), Meta developer tools, and Google Analytics to evaluate three BPM models (manual, AI-driven, and hybrid) against key performance indicators including process efficiency, error reduction, and automation scalability. Empirical findings from real-world case studies and simulations demonstrate that AI integration reduces manual workload by 30–50%, improves targeting accuracy by 25–40%, and minimizes decision-making errors. However, early-stage AI interventions require human feedback to mitigate biases and ensure ethical compliance [10]. The study also addresses gaps in existing literature, such as the lack of practical frameworks for AI-driven BPM in advertising and the need for hybrid models balancing automation with human oversight. Future research directions include leveraging reinforcement learning for AI adaptability and industry-specific tuning. This work contributes a scalable, compliant, and efficient BPM framework for targeted advertising, bridging theoretical and practical gaps in AI-driven process optimization.
ISSN 2959-8109 (Online)













